Beneficence vs. Nonmaleficence: Ethical Balance in Healthcare

In the complex world of healthcare, ethical principles guide decision-making to ensure patient well-being. Two fundamental concepts, beneficence and nonmaleficence, often stand at the forefront of these ethical considerations. While both aim to protect patients, they approach this goal from different angles, creating a delicate balance that healthcare professionals must navigate.
Understanding Beneficence: Doing Good

Beneficence is the ethical principle that obligates healthcare providers to act in the best interest of their patients. It involves taking positive actions to promote health, prevent illness, and restore well-being. For example, recommending a life-saving treatment or providing preventive care aligns with this principle.
💡 Note: Beneficence focuses on proactive measures to enhance patient health, often requiring providers to go beyond the minimum standard of care.
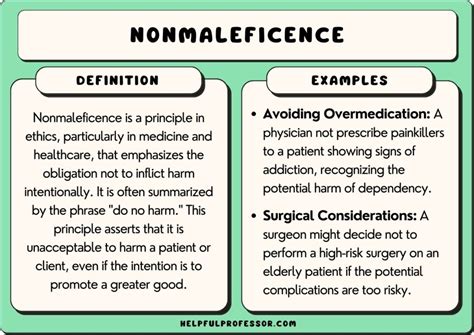
Exploring Nonmaleficence: Avoiding Harm

Nonmaleficence, on the other hand, emphasizes the duty to do no harm. This principle requires healthcare professionals to avoid actions that could cause physical, emotional, or psychological harm to patients. For instance, withholding a treatment with severe side effects or ensuring informed consent before procedures reflects this ethical stance.
⚠️ Note: Nonmaleficence is about minimizing risks and ensuring patient safety, even if it means forgoing certain interventions.
The Ethical Balance: When Principles Collide

The tension between beneficence and nonmaleficence arises when one principle’s application conflicts with the other. For example, a treatment that could save a patient’s life (beneficence) might also carry significant risks (nonmaleficence). Healthcare providers must weigh these considerations carefully, often involving patients in shared decision-making.
| Principle | Focus | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Beneficence | Doing good | Recommending preventive screenings |
| Nonmaleficence | Avoiding harm | Withholding a risky treatment |
Practical Application: Checklist for Ethical Decision-Making
- Assess Risks and Benefits: Evaluate the potential outcomes of each action.
- Involve the Patient: Ensure informed consent and respect patient autonomy.
- Consult Colleagues: Seek input from other professionals for complex cases.
- Document Decisions: Maintain clear records of the reasoning behind choices.
Commercial Insight: Ethical Training for Healthcare Professionals

For healthcare organizations, investing in ethical training programs can help staff navigate these principles effectively. Such programs not only enhance patient care but also reduce legal and reputational risks.
What is the difference between beneficence and nonmaleficence?
+Beneficence focuses on taking positive actions to benefit patients, while nonmaleficence emphasizes avoiding harm.
How can healthcare providers balance these principles?
+Providers should assess risks and benefits, involve patients in decisions, and seek input from colleagues when necessary.
Why is ethical training important for healthcare organizations?
+Ethical training ensures staff can navigate complex decisions, enhancing patient care and reducing risks.
In summary, beneficence and nonmaleficence are cornerstone principles in healthcare ethics, each playing a vital role in patient care. By understanding and balancing these principles, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that prioritize patient well-being. Whether through proactive interventions or careful risk avoidance, the goal remains the same: to provide the highest standard of care. (Healthcare Ethics, Medical Decision-Making, Patient Care)


