What Are Molecular Compounds: A Quick Guide
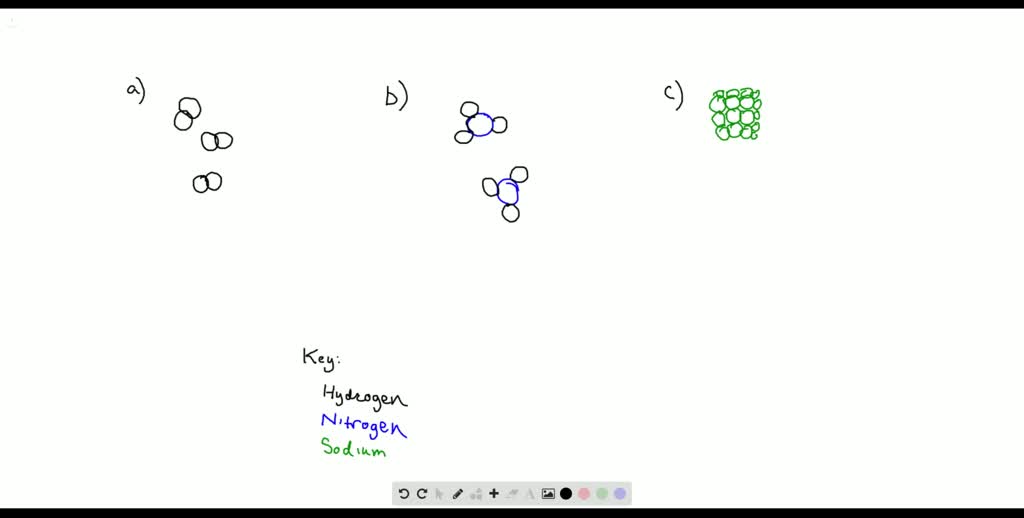
Molecular compounds are substances formed by the chemical bonding of two or more non-metal atoms. These compounds play a crucial role in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. Understanding their structure, properties, and applications is essential for students, researchers, and professionals alike. Whether you're exploring molecular compounds examples or seeking insights into their naming conventions, this guide provides a comprehensive overview tailored to both informational and commercial intent audiences.
What Are Molecular Compounds?

Molecular compounds, also known as covalent compounds, are formed when atoms share electrons to create a stable bond. Unlike ionic compounds, which involve the transfer of electrons, molecular compounds involve covalent bonding. This type of bonding results in discrete molecules with unique properties. Common examples include water (H₂O), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄). These compounds are typically found in the gaseous or liquid state at room temperature, though some may exist as solids.
Key Characteristics of Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds exhibit several distinct features that set them apart from other types of compounds. These include:
- Low melting and boiling points: Due to weak intermolecular forces.
- Poor electrical conductivity: As they do not contain free ions.
- Solubility in non-polar solvents: Most molecular compounds dissolve in organic solvents like ether or benzene.
📌 Note: Molecular compounds are typically insulators, making them unsuitable for electrical applications.
How Are Molecular Compounds Named?

Naming molecular compounds follows specific rules outlined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). The process involves:
- Identifying the elements: List the elements in the compound.
- Using prefixes: Indicate the number of atoms of each element with prefixes like “mono-,” “di-,” “tri-,” etc.
- Writing the name: The first element is named as is, while the second element ends with “-ide.”
For example, CO₂ is named carbon dioxide, where “di-” indicates two oxygen atoms. Understanding these rules is crucial for chemical nomenclature.
Applications of Molecular Compounds

Molecular compounds have a wide range of applications across industries. Some notable uses include:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Medicine | Drugs like aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) |
| Agriculture | Pesticides and fertilizers |
| Technology | Semiconductors and polymers |

For those in the chemical industry, molecular compounds are indispensable for product development and innovation.
Checklist for Understanding Molecular Compounds

To ensure a solid grasp of molecular compounds, follow this checklist:
- Learn the basics of covalent bonding.
- Familiarize yourself with IUPAC naming rules.
- Study common molecular compounds examples.
- Explore their physical and chemical properties.
Molecular compounds are fundamental to understanding chemistry and its applications. From their unique bonding structure to their diverse uses, these compounds are a cornerstone of scientific and industrial advancements. Whether you're a student, researcher, or industry professional, mastering the concepts of molecular compounds will undoubtedly enhance your knowledge and skills in the field of chemistry,molecular compounds examples,chemical nomenclature.
What is the difference between molecular and ionic compounds?
+
Molecular compounds form through covalent bonding, sharing electrons, while ionic compounds involve electron transfer, creating charged ions.
Can molecular compounds conduct electricity?
+
No, molecular compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity due to the absence of free ions.
How are molecular compounds named?
+
Naming follows IUPAC rules, using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms and ending the second element with “-ide.”


